Year 3 Geography: Complete Curriculum Overview for Students and Parents

Year 3 Geography plays a vital role in helping children understand the world around them. At this stage of primary education, students begin to explore places, environments, and people in a more structured and meaningful way. Geography in Year 3 introduces young learners to both physical and human features of the world, encouraging curiosity and awareness of how humans interact with their surroundings. It also supports essential skills such as observation, map reading, and basic enquiry, which are useful across many subjects.
For parents and teachers, understanding what is taught in Year 3 Geography helps support children’s learning more effectively. The subject is designed to be engaging and practical, combining classroom learning with hands-on activities such as map work and local area studies. By the end of Year 3, pupils are expected to have a stronger sense of place, improved geographical vocabulary, and a growing awareness of environmental responsibility.
Understanding the Year 3 Geography Curriculum
The Year 3 Geography curriculum is aligned with the national primary education framework, focusing on developing foundational geographical knowledge and skills. At this level, children are encouraged to ask questions about the world, observe their surroundings, and compare different places. The curriculum aims to build confidence in understanding locations, environments, and basic geographical processes.
One of the key strengths of Year 3 Geography is its cross-curricular approach. Geography is often linked with subjects such as science, history, and literacy, allowing children to make meaningful connections. For example, learning about weather links naturally with science, while studying local areas can connect to history and writing activities. This integrated approach helps reinforce learning and keeps students engaged.
The main learning objectives in Year 3 Geography include developing location knowledge, understanding physical and human geography, and building enquiry skills. Pupils learn to describe places using simple geographical language and begin to understand how environments differ across the world. These objectives prepare students for more detailed geographical study in later years.
Physical Geography in Year 3
Physical geography is a core component of Year 3 Geography and focuses on natural features and processes. One of the main topics children explore is weather and climate. Students learn to identify different types of weather, understand seasonal changes, and observe how weather affects daily life. Simple concepts such as temperature, rainfall, and wind are introduced in an age-appropriate way, often through charts, drawings, and daily observations.
Another important area is the study of landforms and natural features. Children are introduced to mountains, rivers, valleys, and coasts, learning how these features are formed and why they are important. Lessons often include pictures, videos, and models to help students visualise these features. This helps children understand that the Earth’s surface is varied and constantly changing due to natural processes.
The water cycle is also a key topic in Year 3 Geography. Pupils learn about evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and collection through simple explanations and diagrams. Understanding the water cycle helps children see how water moves through the environment and why it is essential for life. Teachers often use experiments and real-life examples to make this topic engaging and easy to understand.
Human Geography in Year 3
Human geography helps children understand how people live, work, and interact with their environment. In Year 3 Geography, students explore settlements and land use, learning the differences between villages, towns, and cities. They also discuss how land is used for housing, farming, transport, and industry. This helps children recognise how human needs shape the landscape.
Transport and trade are also important topics within human geography. Children learn about different types of transport, such as roads, railways, ships, and aeroplanes, and why transport is important for moving people and goods. Simple discussions about where food and products come from help students understand trade in a basic but meaningful way.
Environmental awareness is increasingly emphasised in Year 3 Geography. Pupils learn about caring for the environment, recycling, and reducing waste. Teachers encourage children to think about how human actions affect the planet and what they can do to protect it. This early focus on sustainability helps build responsible attitudes toward the environment that can last a lifetime.
Geographical Skills and Fieldwork
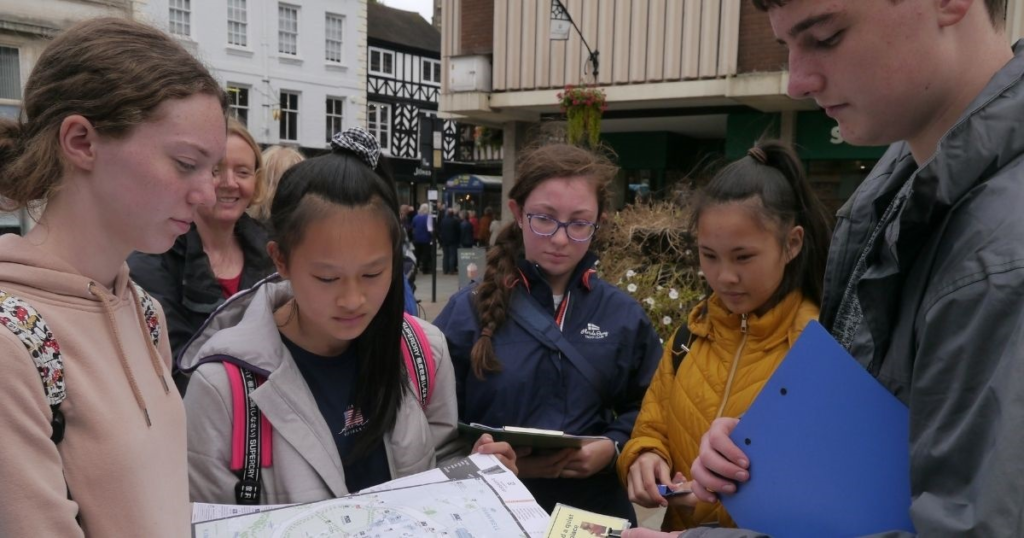

Developing geographical skills is a major focus of Year 3 Geography. One of the most important skills taught is map reading. Children learn to read simple maps, understand symbols, and use basic directions such as north, south, east, and west. They may also be introduced to simple compass use, helping them develop spatial awareness.
Students also learn how to collect and use data in geography. This includes making observations, carrying out simple surveys, and recording information using charts and diagrams. Pupils may use globes, atlases, and digital maps to explore different places, helping them understand the wider world beyond their local area.
Fieldwork is an exciting part of Year 3 Geography. Local area studies allow children to explore their surroundings, observe physical and human features, and ask geographical questions. These practical activities make learning more engaging and help students apply their classroom knowledge in real-world contexts. Fieldwork also develops confidence, teamwork, and enquiry skills.
Teaching and Learning Strategies
Effective teaching strategies are essential for successful Year 3 Geography learning. In the classroom, teachers use interactive activities such as group discussions, map work, videos, and storytelling to keep students engaged. Visual aids and hands-on resources help simplify complex ideas and make lessons more enjoyable.
Home learning also plays an important role. Parents can support Year 3 Geography by encouraging children to talk about what they have learned, helping with homework, and exploring maps or globes together. Simple activities such as discussing the weather or planning a journey can reinforce geographical concepts at home.
Assessment in Year 3 Geography is usually informal and ongoing. Teachers assess learning through observations, classwork, quizzes, and discussions. The focus is on understanding and skill development rather than formal testing. This approach helps identify areas where children may need extra support and ensures steady progress throughout the year.
Conclusion
Year 3 Geography provides a strong foundation for understanding the world and our place within it. Through a balanced mix of physical geography, human geography, and practical skills, children develop curiosity, awareness, and essential learning abilities. The subject encourages students to ask questions, explore environments, and think critically about how people and nature interact.
By building knowledge gradually and engaging students through real-life examples, Year 3 Geography prepares children for more advanced learning in later years. It also fosters environmental responsibility and global awareness, helping young learners grow into informed and thoughtful individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is taught in Year 3 Geography?
Year 3 Geography covers physical geography, human geography, map skills, and local area studies.
How does Year 3 Geography fit into the national curriculum?
It follows national guidelines designed to build foundational geographical knowledge and skills.
What skills do children learn in Year 3 Geography?
Children learn map reading, observation, enquiry, data collection, and environmental awareness.
How can parents help with Year 3 Geography at home?
Parents can discuss topics, explore maps, and encourage curiosity about places and environments.
What are examples of Year 3 Geography fieldwork activities?
Local walks, observing weather, mapping the school area, and simple surveys.
How are map skills introduced in Year 3 Geography?
Through simple maps, symbols, compass directions, and practical activities.
What is the difference between human and physical geography?
Physical geography focuses on natural features, while human geography studies how people live and use land.
How is Year 3 Geography assessed?
Assessment is informal, based on classwork, discussions, and teacher observations.
Why is geography important for Year 3 students?
It builds awareness of the world, critical thinking skills, and environmental responsibility.
How does Year 3 Geography prepare children for later learning?
It lays the groundwork for advanced geographical concepts and enquiry skills in higher years.
You May Also Read: Islay News