GCSE Maths Differentiation: Complete Beginner’s Guide with Examples
GCSE Maths differentiation is one of the most important topics students encounter when moving from basic algebra into more advanced mathematical thinking. At its core, differentiation is about understanding how things change. In GCSE Mathematics, it is introduced in a simplified and accessible way so that students can grasp the fundamental ideas without being overwhelmed by advanced calculus. Whether you are aiming for a pass at Foundation tier or pushing for top grades at Higher tier, differentiation plays a key role in exam success.
Many students initially find GCSE Maths differentiation intimidating because it involves new language, symbols, and problem-solving techniques. However, when broken down step by step, differentiation becomes much more manageable. It builds on knowledge students already have, such as algebra, graphs, and gradients. By learning differentiation, students develop skills that help them analyse problems logically, interpret graphs accurately, and solve real-life mathematical situations.
Differentiation also has strong relevance beyond exams. It helps explain concepts like speed, growth, and change, which are used in science, economics, and engineering. For GCSE students, mastering differentiation is not just about passing exams but about building confidence in handling more complex mathematical ideas. With clear explanations, regular practice, and the right revision strategies, GCSE Maths differentiation can become one of the most rewarding topics to learn.
Understanding the Concept of Differentiation
At GCSE level, differentiation is best understood as finding the rate at which something changes. In simple terms, it tells us how fast one quantity is changing compared to another. For example, differentiation can help determine how steep a curve is at a specific point or how quickly a value is increasing or decreasing. This idea of change is central to many areas of mathematics and science, making differentiation a powerful and practical tool.
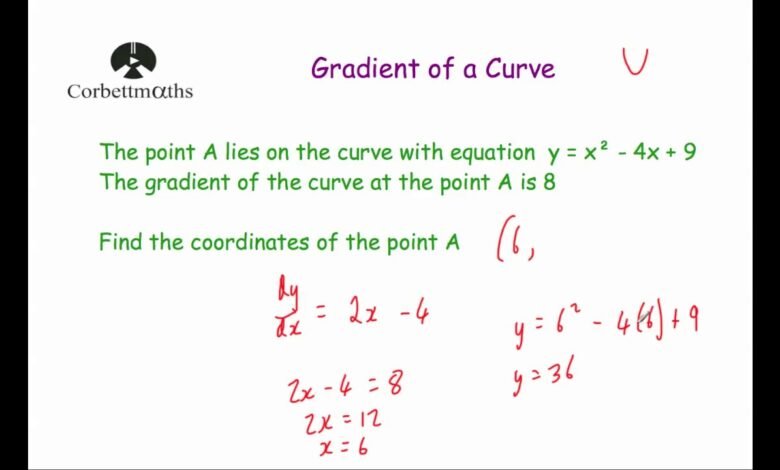
One of the most common interpretations of differentiation in GCSE Maths is its link to gradients. When working with straight lines, students learn how to calculate gradients using basic formulas. Differentiation extends this idea to curves. Instead of having one constant gradient, a curve has a changing gradient, and differentiation allows students to find the gradient at any chosen point on that curve.
Another important concept is the difference between average and instantaneous rate of change. While average change looks at how something changes over a range, differentiation focuses on what is happening at a single point. This idea is often explained visually using tangents to curves. By understanding these core concepts early, students can approach GCSE Maths differentiation questions with greater clarity and confidence.
Basic Differentiation Rules in GCSE Maths
GCSE Maths differentiation is built around a small set of clear and straightforward rules. These rules allow students to differentiate a wide range of algebraic expressions quickly and accurately. One of the first rules students learn is that constants differentiate to zero. This means that any number without a variable has no rate of change, which is a simple but crucial concept.
The most important rule in GCSE differentiation is the power rule. This rule states that when differentiating a term like xⁿ, you multiply by the power and reduce the power by one. For example, x² becomes 2x, and x³ becomes 3x². This single rule forms the foundation of most differentiation questions at GCSE level and is essential for both Foundation and Higher tier exams.
Students also learn how to differentiate expressions with coefficients, such as 5x² or -3x³. In these cases, the coefficient stays the same while the power rule is applied. By practising these basic rules regularly, students can quickly build speed and accuracy. Mastery of these fundamentals makes more complex GCSE Maths differentiation questions much easier to handle in exams.
Differentiation of Common Algebraic Functions
In GCSE Maths differentiation, students are expected to confidently differentiate common algebraic functions, particularly polynomials. These include expressions involving powers of x, such as x², x³, and higher powers. By applying the power rule consistently, students can simplify and differentiate even complex-looking expressions with ease.
Another important skill is differentiating expressions with fractions and negative powers. For example, 1/x can be rewritten as x⁻¹ before differentiating. This highlights the importance of algebraic manipulation before applying differentiation rules. Simplifying expressions first often reduces errors and helps students present clear, well-structured solutions in exams.
GCSE Maths differentiation questions may also include multiple terms in a single expression. Students must differentiate each term separately and then combine the results. This reinforces earlier algebra skills and encourages careful working. With regular practice, students can develop a systematic approach that ensures accuracy and earns full marks in exam questions.
Differentiation Using Graphs
Graphs play a vital role in GCSE Maths differentiation, helping students visualise abstract concepts. One of the key ideas is that differentiation gives the gradient of a curve at a specific point. This gradient represents how steep the curve is at that location and whether it is increasing or decreasing.
To find the gradient at a point on a curve, students often draw a tangent and calculate its gradient. This graphical method helps reinforce the connection between algebraic differentiation and visual interpretation. Understanding this link is especially useful for exam questions that combine graphs and algebra.
Interpreting gradients correctly is essential. A positive gradient means the curve is rising, while a negative gradient shows it is falling. A gradient of zero indicates a turning point. By practising graph-based differentiation questions, students improve their ability to analyse curves and explain their reasoning clearly, which is a valuable skill in GCSE exams.
Applications of Differentiation in GCSE Maths
One of the most important applications of GCSE Maths differentiation is finding maximum and minimum points. These turning points often appear in optimisation problems, where students must find the best possible solution under given conditions. Differentiation helps identify these points by finding where the gradient is zero.
Real-life applications make differentiation more meaningful and engaging. GCSE questions may involve scenarios such as maximising area, minimising cost, or analysing speed and distance. These problems test not only mathematical skills but also the ability to interpret information and apply methods logically.
Understanding applications of differentiation helps students see why the topic matters beyond exams. It encourages deeper thinking and problem-solving, which are key skills assessed in higher-grade GCSE questions. With practice, students can approach application-based questions with confidence and precision.
GCSE Differentiation Exam Questions and Techniques

GCSE Maths differentiation questions come in various forms, including straightforward differentiation, graph interpretation, and problem-solving tasks. Knowing how to approach each type is essential for exam success. Clear working and logical steps are often rewarded, even if the final answer is not perfect.
A structured approach is key. Students should simplify expressions first, apply differentiation rules carefully, and check their answers. Understanding command words such as “find,” “calculate,” and “show that” helps students respond appropriately and avoid losing marks unnecessarily.
Time management is also important. Differentiation questions can be quick to answer if students are confident with the rules. Regular practice under timed conditions helps build speed and reduces exam stress, leading to better overall performance.
Common Mistakes Students Make in Differentiation
One common mistake in GCSE Maths differentiation is forgetting to reduce the power correctly when applying the power rule. Small errors like this can lead to incorrect answers, even if the method is mostly right. Careful checking can help avoid these issues.
Another frequent error is not simplifying expressions before differentiating. This can make the process more complicated and increase the chance of mistakes. Encouraging neat, organised working helps students stay focused and accurate.
Misinterpreting graphs is also a challenge for many students. Confusing gradients or misreading scales can lead to incorrect conclusions. Practising a wide range of questions helps students recognise and avoid these common pitfalls.
Foundation vs Higher Tier Differentiation
GCSE Maths differentiation appears differently in Foundation and Higher tier exams. Foundation tier focuses on basic rules and simple applications, while Higher tier includes more complex expressions and problem-solving tasks. Understanding these differences helps students target their revision effectively.
Higher tier students may encounter more challenging optimisation problems and algebraic manipulation. Foundation tier students, on the other hand, should focus on mastering the basics and applying rules confidently. Both tiers reward clear working and accurate application of methods.
By knowing what is expected at each level, students can tailor their preparation and avoid unnecessary stress. Targeted practice ensures steady progress and improved exam performance.
Revision Strategies for GCSE Maths Differentiation
Effective revision is essential for mastering GCSE Maths differentiation. Regular practice, rather than last-minute cramming, helps reinforce understanding and build confidence. Using a variety of questions ensures exposure to different problem types.
Past papers and mark schemes are particularly valuable. They show how questions are structured and how marks are awarded. Reviewing mistakes and learning from them is one of the most effective ways to improve.
Combining revision techniques, such as flashcards for rules, practice questions, and visual aids like graphs, caters to different learning styles. A balanced approach makes revision more engaging and productive.
Conclusion
GCSE Maths differentiation is a powerful topic that develops both mathematical skill and logical thinking. By understanding the core concepts, mastering the rules, and practising regularly, students can approach differentiation with confidence. From basic gradients to real-life applications, differentiation plays a crucial role in exam success and beyond. With the right strategies and mindset, any student can excel in GCSE Maths differentiation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is differentiation in GCSE Maths?
Differentiation is the process of finding the rate of change or gradient of a function.
Is differentiation included in Foundation GCSE Maths?
Yes, basic differentiation appears in Foundation tier, while more advanced topics are in Higher tier.
How difficult is GCSE Maths differentiation?
It is manageable with practice and a clear understanding of the rules.
What is the most important differentiation rule to remember?
The power rule is the most important rule at GCSE level.
How can I improve quickly at differentiation?
Regular practice, reviewing mistakes, and using past papers are the best ways to improve.
You May Also Read: BBC Bitesize KS3 Photosynthesis