Iran Cities Guide: Complete List of Major and Historic Cities
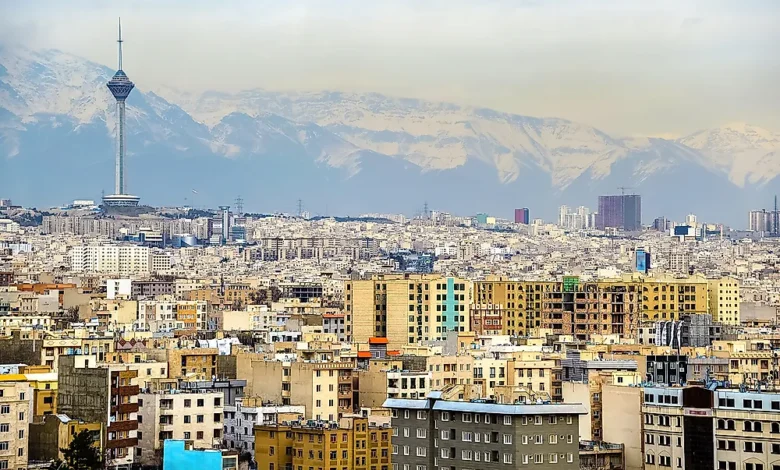

Iran cities represent one of the oldest continuous urban traditions in the world, shaped by thousands of years of civilization, conquest, trade, and cultural exchange. From ancient settlements that once stood at the heart of powerful empires to modern metropolitan centers driving economic and technological growth, Iranian cities offer a unique blend of history and progress. Each city reflects the geography, culture, and historical influences of its region, making Iran’s urban landscape remarkably diverse and layered.
Today, Iran cities are not just population centers; they are cultural storytellers. Cities like Tehran, Isfahan, Shiraz, and Mashhad function as political, artistic, spiritual, and economic hubs respectively. At the same time, smaller cities preserve local traditions, languages, and lifestyles that continue to thrive alongside modernization. Understanding Iran cities provides valuable insight into the country’s identity, social structure, and future development.
Historical Development of Iran Cities
The history of Iran cities dates back several millennia, beginning with ancient settlements that flourished due to fertile land, water access, and trade routes. Cities such as Susa, Persepolis, and Ecbatana played crucial roles during the Achaemenid Empire, showcasing advanced urban planning, monumental architecture, and administrative systems. These early cities were not only political capitals but also cultural and economic powerhouses connecting East and West.
During the Islamic era, Iran cities underwent significant transformation. Mosques, madrasas, bazaars, and caravanserais became defining elements of urban life. Cities like Isfahan reached their architectural peak under the Safavid dynasty, earning global recognition for their city planning and artistic achievements. Despite invasions and political shifts, Iranian cities consistently adapted, preserving historical layers while embracing new influences that shaped their evolution.
Major Iran Cities and Their Significance
Tehran, the capital of Iran, stands as the country’s political, economic, and cultural nerve center. As the largest city, it hosts government institutions, major industries, universities, and media outlets. Tehran’s rapid expansion reflects Iran’s modern ambitions, while its museums, palaces, and cultural districts preserve national heritage. The city’s diverse population also mirrors the multicultural nature of the country.
Other major Iran’cities hold equally important roles. Mashhad is a spiritual center attracting millions of pilgrims annually, Isfahan is celebrated for its stunning Islamic architecture, Shiraz is known for poetry and gardens, and Tabriz serves as a major industrial and commercial hub. Each of these cities contributes uniquely to Iran’s national identity, highlighting how urban centers specialize in different aspects of cultural, religious, and economic life.
Iran Cities by Region and Geography
Geography plays a vital role in shaping Iran cities. Northern cities near the Caspian Sea, such as Rasht and Sari, benefit from lush landscapes, agriculture, and milder climates. These cities contrast sharply with central plateau cities like Yazd and Kashan, which have developed innovative architectural solutions to survive desert conditions, including windcatchers and underground water systems.
Western Iran cities are often located in mountainous regions and are known for their ethnic diversity and historical resilience. Meanwhile, southern port cities such as Bandar Abbas and Bushehr connect Iran to global maritime trade routes. This regional variation makes Iran’cities geographically diverse, each adapted to its environment while contributing to national cohesion.
Cultural Diversity in Iran Cities
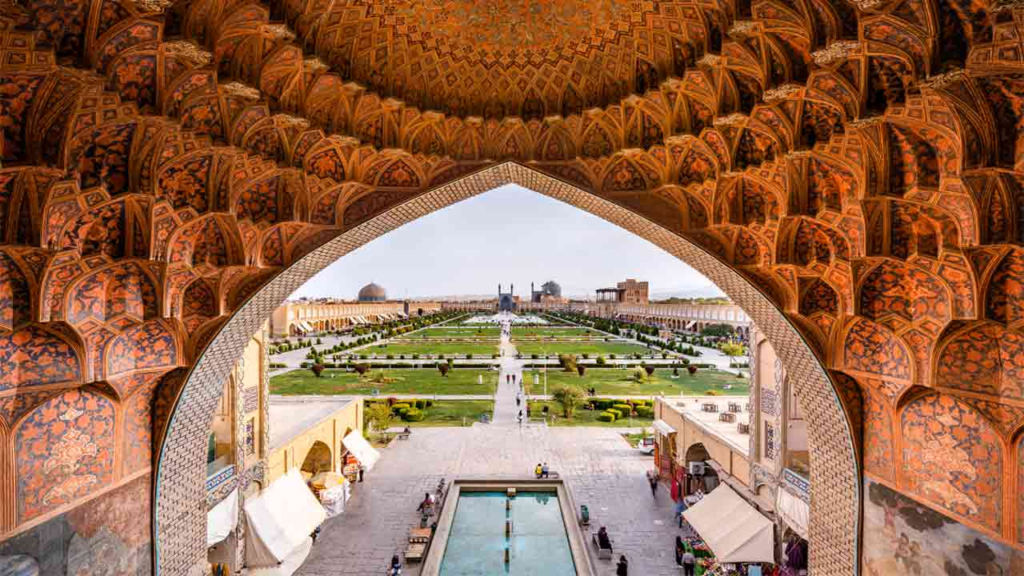

Iran cities are home to a wide range of ethnic groups, languages, and traditions. Persian culture forms the foundation, but many cities reflect Azeri, Kurdish, Arab, Baluchi, and Turkmen influences. This diversity enriches urban life through music, clothing, festivals, and cuisine, giving each city a distinct cultural character.
Religion also shapes city culture, particularly in cities like Mashhad and Qom, where religious institutions influence daily life and urban design. Traditional values coexist with modern lifestyles, creating a dynamic cultural balance. Markets, public squares, and cultural centers remain vital social spaces where heritage and contemporary expression meet.
Economic and Industrial Role of Iran Cities
Economically, Iran cities function as engines of national growth. Tehran dominates finance, administration, and services, while cities like Isfahan and Tabriz are major industrial centers. Oil and gas-related cities in the south play a critical role in Iran’s energy sector, supporting national and regional economies.
Trade, manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism all rely heavily on urban infrastructure. Many Iran’cities are also centers for handicrafts, textiles, and traditional industries that contribute to both local employment and international cultural recognition. Together, these cities form a diversified economic network sustaining the country’s development.
Modernization and Urban Growth in Iran Cities
Modernization has rapidly transformed Iran cities over the past few decades. Population growth, rural-to-urban migration, and infrastructure expansion have reshaped city landscapes. Highways, metro systems, universities, and technology parks reflect Iran’s push toward modernization and innovation.
However, this growth also brings challenges such as traffic congestion, pollution, housing shortages, and sustainability concerns. Urban planners increasingly focus on smart city initiatives, green spaces, and public transport improvements. Balancing development with cultural preservation remains a key priority for the future of Iran cities.
Tourism and Travel in Iran Cities
Tourism plays a growing role in many Iran cities, attracting visitors interested in history, architecture, and culture. Cities like Isfahan, Shiraz, and Yazd are internationally recognized for their heritage sites, while Tehran offers museums, galleries, and modern attractions. Traditional bazaars, mosques, and gardens provide immersive cultural experiences.
In addition to historical tourism, natural attractions near cities—such as mountains, deserts, and coastlines—enhance travel appeal. Hospitality, local cuisine, and cultural etiquette contribute to memorable experiences for visitors. Iran’cities continue to gain recognition as unique travel destinations blending authenticity with depth.
Conclusion
Iran cities collectively tell the story of a nation shaped by ancient civilizations and modern aspirations. Each city, whether historic or contemporary, contributes to Iran’s cultural richness, economic strength, and social diversity. From architectural masterpieces to bustling modern streets, these cities embody resilience and creativity.
As Iran moves forward, its cities remain central to balancing tradition with progress. Understanding Iran cities offers not only geographical knowledge but also a deeper appreciation of the country’s identity, heritage, and future potential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the largest cities in Iran by population?
Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, Karaj, and Shiraz are among the largest Iran cities.
Which Iran cities are best for tourists?
Isfahan, Shiraz, Yazd, Tehran, and Tabriz are popular tourist destinations.
How many cities are there in Iran?
Iran has hundreds of officially recognized cities across its provinces.
What is the oldest city in Iran?
Cities like Susa are among the oldest continuously inhabited settlements.
Are Iran cities safe for travelers?
Many Iran cities are considered safe, especially major tourist destinations.
Which Iran city is the economic center?
Tehran is the primary economic and financial hub of Iran.
What languages are spoken in different Iran cities?
Persian is the official language, with regional languages spoken in various cities.
You May Also Read: Alpaca or Llama